Advanced Example HGCal_testbeam
Responsible Geant4 Collaborator and developer: Anna Zaborowska (CERN, Geneva, Switzerland)
Short description
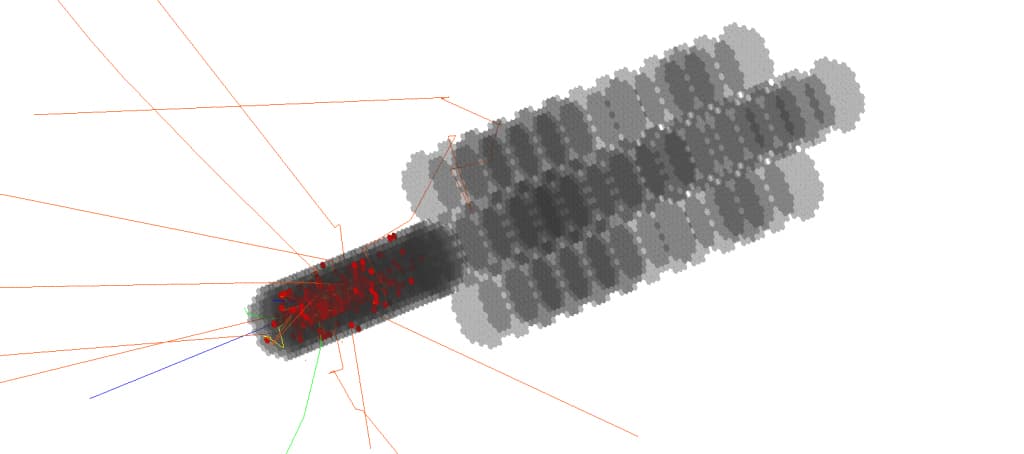
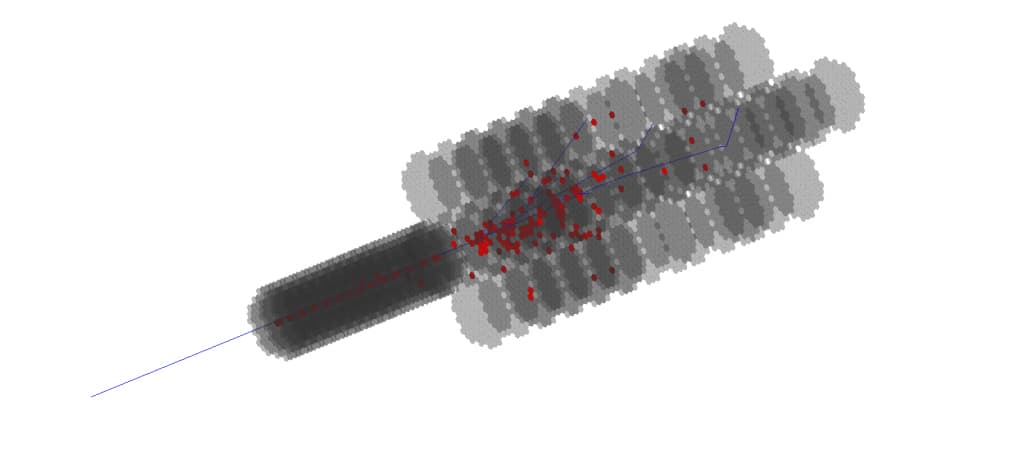
HGCal_testbeam example is a demonstration of a high-end High Energy Physics test beam setup, for the endcap electromagnetic calorimeter of the CMS detector CERN-LHCC-2017-023. It will be used as a base for the regular Geant4 physics validation studies performed within geant-val.
This example is based on the Geant4 standalone application developed by Thorben Quast for the CMS HGCal studies (link).
The implemented geometry is simplified with respect to the geometry studied by the CMS Collaboration within their software framework, however, it offers a detailed description of the detector. It presents a test beam setup used in the HGCal studies in October 2018. It can be easily extended to other configurations thanks to the modularity of the detector geometry definition.
A dictionary of possible elements (logical volumes) is created, and a configuration describes which volumes are placed along the z-axis. Example of a configuration including HGCal and the beamline elements (upstream material) is provided, as well as a test geometry consisting of a single silicon wafer with absorbers.
The Geant4 Particle Gun is used in the example as the default source of primary particles. For the physics validation, primary particles can be read from the ROOT file. In the simulation energy deposited in the sensitive layers of the detector (silicon pixels) is registered, and digitised at the end of each event. The output of the simulation is stored in an ntuple in a ROOT file.
Last updated: 15/02/2022 by S. Guatelli